1.8 TSI/TFSI EA888 motor was first manufactured by Audi AG in 2007. EA888 1.8 TSI plus 2.0 TSI were constructed as alternatives to 1.8 and 2.0L motors from the EA113 lineup.
Being a 4-cylinder gasoline engine featuring a turbocharger and direct fuel injection, this motor was modernized three times. So, let’s find out a bit more about its variations.
Engines of the 3rd generation EA888 series were launched in 2011 for Audi cars, and in 2012 they reached VW, SEAT, and Skoda. This generation replaced the EA888 2nd generation (CDA and CDH) and had many differences from 888/2
A lightweight closed cylinder block appeared with 48 mm crankshaft supports and slightly thinner cylinder walls. A light crankshaft with 4 counterweights, modified connecting rods and pistons were installed in the block.
1.8 TSI Engine Specs
| Manufacturer | Volkswagen AG |
| Production years | 2007 – present day |
| Cylinder block material | Cast Iron |
| Cylinder head material | Aluminum |
| Fuel type | Gasoline |
| Fuel system | Direct fuel injection; Direct injection + multi-point injection |
| Configuration | Inline |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Valves per cylinder | 4 |
| Valvetrain layout | DOHC |
| Bore, mm | 82.5 (3.25 in) |
| Stroke, mm | 84.1 (3.31 in) |
| Displacement, cc | 1,798 (109.7 cu in) |
| Type of internal combustion engine | Four-stroke, turbocharged |
| Compression Ratio | 9.6:1 |
| Power, hp (horsepower) | 120-170 (88-125kW)/ 4,000-6,200 |
| Torque, lb ft | 170-240 (230-320 Nm)/ 1,500-4,800 |
| Engine weight | 144 kg (318 lbs) |
| EA888 Firing order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Engine oil weight | VW 502 00; SAE 5W-30, 5W-40 |
1.8 TSI EA888 Engine Problems and Reliability
All kinds of 1.8 TSI EA888 face trouble with timing chain stretching after approximately 60,000 miles (100,000 kilometers). Signs of this malfunction are noise and unsteady functioning while consequences may deal with a serious motor breakdown. The 3rd generation keeps another tensioner and has fewer chances for such dysfunction.
Unlike Generation 1 and 3, the 2nd generation tends to have trouble with excessive oil use, induced by thin piston rings. Moreover, with time, the motor starts to use more oil. It can consume about 2 liters by 1,000 kilometers after a motor run around 100,000 kilometers (60,000 miles). It’s advisable to exchange pistons for the ones of the debut modification.
In Generation Three motors, a turbocharger actuator must be regulated after the motor runs more than 100,000 kilometers (60,000 miles).
Motors with direct injection often face trouble with charcoal, appearing on intake valves plus intake ports. Fuel gets straight to the cylinder instead of being injected into the port and washed out the carbon deposit. As a consequence of that, airflow is restricted in addition to overloaded valves and inefficient closing gaps.
The motor uses more fuel, producing less output. However, Generation 3 engines avoid this trouble thanks to keeping fuel injection into the ports along with direct injection.
On the whole, 1.8 TSI EA888 motors aren’t the most durable and can face many problems, including excessive oil use and timing chain malfunction. Basically, it’s the fault of Generation Two as it’s the most widespread engine of the series.
Nevertheless, the motors of this series are pretty reliable. They have great output and torque, consuming less fuel than their rivals. Tuning can be made to all motors through an easy Electronic Control Unit remap (Stage 1). After Stage 2 and 3, motors have more effective exhaust, output turbocharger, and updated Electronic Control Unit.
That leads to outstanding power and torque. Identical to other turbocharged motors with direct injection, this one demands oil and fuel of good quality, periodical, and efficient service. If you take care of the motor, it will serve you for 150,000-200,000 miles (250,000-300,000 kilometers) and even more. However, Generation Two may need some adjustments or repairs after a 60,000-80,000 miles run.
More info – https://vwtuning.co/vw-ea888-engine-problems/
What Cars Have A VW EA888 1.8 Engine?
Which vehicles come equipped with EA888 1.8 TSI engines?
- VW Jetta Mk5/Sagitar
- VW Passat B6
- VW Passat CC
- Audi TT Mk2 (8J)
- Audi 8P A3
- Audi B7 A4
- Audi A4 (B8)
- Audi A5
- SEAT Leon Mk2 (1P)
- SEAT Altea XL
- Skoda Yeti
- Skoda Octavia Mk2 (1Z, Ming Rui)
- Skoda Superb Mk2 (3T)
1.8 TSI EA888 Gen 1
Serving as a substitute to 2.0 TSI EA113 and being manufactured till 2010, the debut version of 1.8 TSI motor with BYT and BZB codes was built from scratch. Its only identical characteristic to its forerunner remains the 88 mm (3.46 inches) cylinder spacing.
The cylinder block and crankcase are made of grey cast iron, which is highly-productive and enduring, along with outstanding acoustic dampening features. To decrease vibration, the crankcase comprises 2 chain-driven counter-rotating balance shafts. Having 220 mm block height, 1.8 TSI Generation One gained steel crankshaft with 8 counterbalances, updated aluminum pistons plus connecting rods of 148 mm.
The motor keeps a 16-valve cylinder head (having 2 intake and 2 exhaust valves for each cylinder) with chain-driven dual overhead camshafts while the intake camshaft features a variable intake valve timing control system. The diameter of the intake valve is 34 mm while the exhaust one is 28 mm and the stem diameter for both of them is 6 mm. Low-friction roller finger cam followers operate valves, containing automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation.
Keeping variable-length plastic intake manifold, the debut generation of motors gained BorgWarner KKK K03 turbocharger with water cooling, placed in cast iron exhaust manifold and having maximal boost pressure of 0.6 bar (8.7 psi). Gasoline is supplied via a direct fuel injection system, having consistent fuel injectors with 6 holes run by a solenoid.
The electronic control unit is Bosch Motronic MED 17.5. Simultaneously, 1.8 TFSI motors, applied for Audi cars with CABA, CABB and CABD codes, got Fuel Stratified system and variable oil pump.
1.8 TSI EA888 Gen 2
As the first generation wasn’t perfect, the brand continued to optimize this engine in 2008 and created TSI EA888 Generation Two, which was produced till 2015. Though this motor was manufactured along with its predecessor for two years, it became the most popular modification.
The motor gained an updated steel crankshaft with CDAA, CDHA, and CDHB codes while the main journal diameter decreased from 58 mm to 52 mm.
Modernized pistons and piston rings were added but served as the main reason for excessive oil consumption. Consequently, motors were built with variable oil pumps. But everything else, except for some minor elements and Electronic Control Unit tuning, is similar to the 1st generation.
1.8 TSI EA888 Gen 3
Manufacture of the 3rd generation of 1.8 TSI EA888 was launched in 2011. Initially, these motors were utilized for Audi automobiles, but afterward, some other VW Group vehicles were supplied with them. Generation 3 motors appeared after numerous modifications and were similar to the 2nd generation.
1.8 TSI EA888 Generation 3 features fresh lightweight cylinder block with thin walls, light but enduring camshaft with 4 counterbalances, redeveloped pistons plus rods. The upgraded cylinder head is a distinctive feature of the motor. An aluminum cylinder head with a dual overhead camshaft and 16 valves comprises an integrated exhaust manifold.
A variable valve timing system operates intake and exhaust valves. Additionally, the 2-stage valve lift control turns on after 3,100 rpm. While no changes were made to the timing chain, another chain tensioner was applied.
The fuel system contains direct fuel injection inside combustion chambers along with classic multipoint fuel injection before intake valves. The motor keeps IHI IS12 turbocharger with the maximum boost pressure of 1.3 bar (18.8 psi).
Motors with CJEB, CJEE, and CJED codes are located longitudinally while CJSA is placed transversally. Nine times out of ten, 4-wheel drive automobiles feature CJSB engines. Meanwhile, CPKA and CPRA are the prevalent motors in the American and Canadian markets.
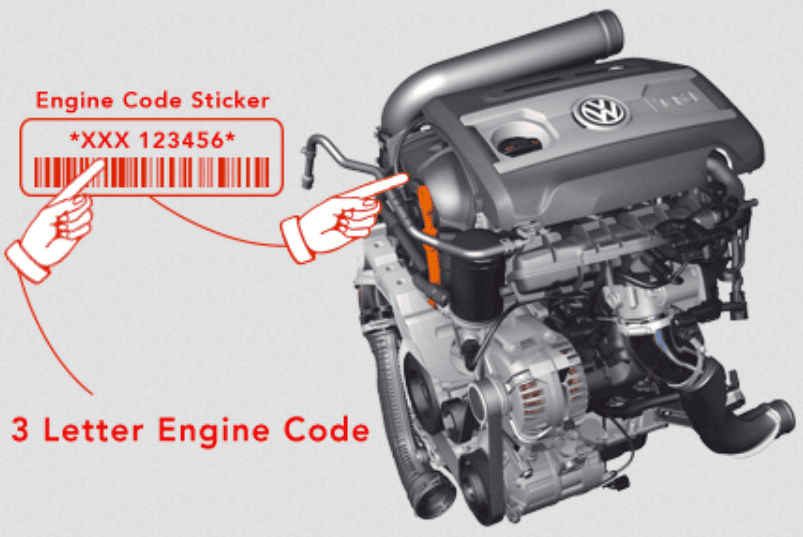
Where Is The Engine Code On A VW EA888 Located?